April 11th 2022
GIA Certificates: How to read them and what to avoid
By Devin Jones
GIA certificates include a variety of information, but they can quickly become confusing for the uninitiated. Here's a quick guide to evaluating your GIA Diamond Grading Report.
Below we'll discuss:
- What are GIA Grading Reports?
- Basic Diamond Information (GIA Report Number, Shape, Cutting Style, Measurements)
- GIA Grading Results (Carat, Color, Clarity, Cut)
- Additional Grading Info (Polish, Symmetry, Fluorescence)
- Inclusions (Key To Symbols, Diamond Plot, Comments)
- Diamond Proportions (Table, Depth, Pavilion Angle, Crown Angle, Girdle Thickness)
- Grading Scales
🛡️ Check your diamond 💎 Search 2M+ diamonds
GIA Diamond Grading Reports
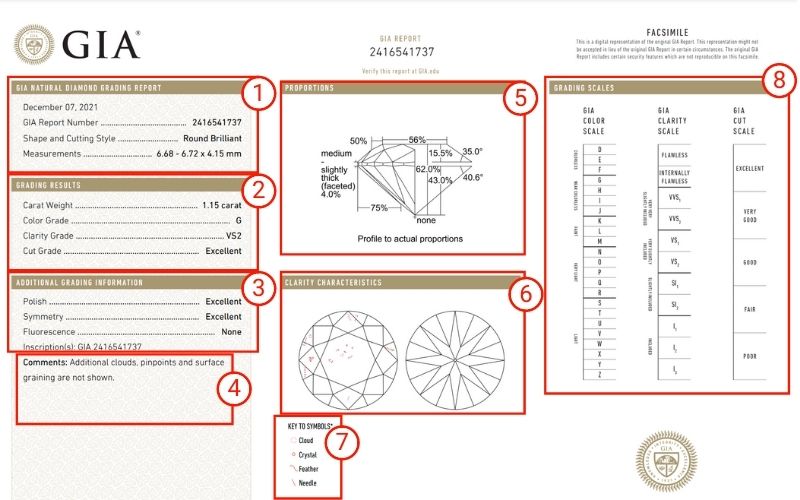
GIA diamond gradings generally look like the below image showing the 8 distinct sections we'll cover in more detail below. Each report has a special ID number that is listed at the top center of the certificate under the words "GIA Report" and on the left hand side in the section titled GIA Natural Diamond Grading Report (#1 below). This GIA number is unique to each diamond and is often laser inscribed on the side of the diamond in tiny print along the diamond's girdle.
Take the below report which comes from this diamond (GIA 2416541737) available from Blue Nile. We've added notation that will help us study the report easier as we go...
Click on the certificate for more details and images of GIA 2416541737
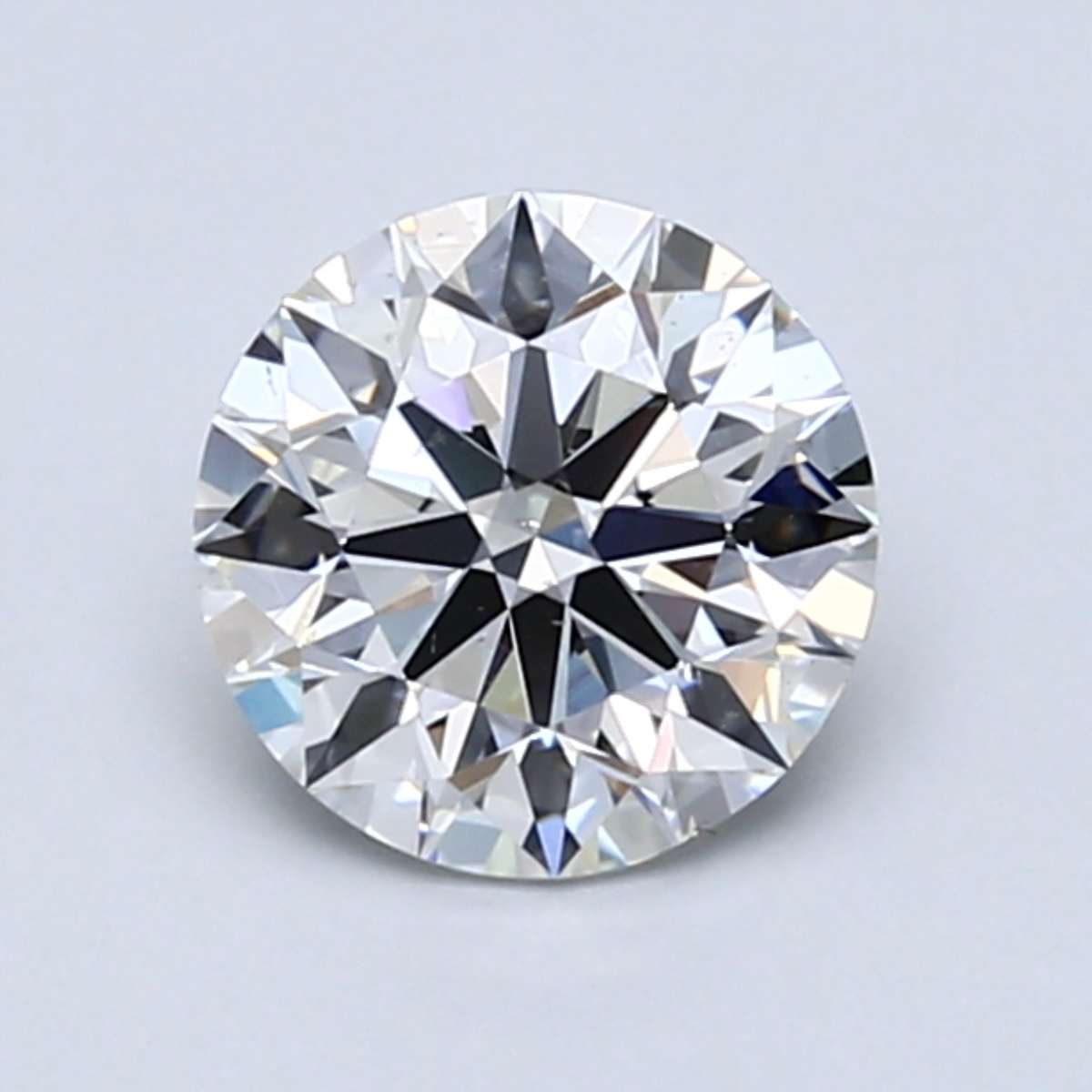
Here's what the diamond actually looks like...
Click on the diamond for more details and videos
The GIA number is a powerful code that allows you to unlock special information about your diamond digitally as well.
If you have a diamond that you want to investigate further, you can run it through StoneAlgo's free GIA Check Tool to see our ratings for diamond cut score, visual carat weight, and diamond price to help you find your perfect diamond.
Let's go through the above information to understand what information is most crucial to evaluating your diamond.
Need help understanding your diamond? Use our free check tool...
1. Basic Diamond Information of the GIA Grading Report
The first section of the report on the left hand side provides some basic information including:
- GIA Report Number: your diamond's unique identifier which ties the physical diamond to the GIA's grade for the stone
- Shape & Cutting Style: describes the diamond's appearance both in terms of shape (round, oval, pear, etc.) and cutting style (some shapes like cushion cut diamonds have a variety of styles such as Brilliant, Modified Brilliant, and Old Mine Brilliant)
- Measurements: these list the length, width, and depth of your diamond in that order. Diamond measurements shown are in millimeters.
Advice: The shape and cutting style of your diamond are totally a matter of preference. Some people love round cut diamonds (the most popular diamond shape by far) while others prefer more exotic shapes like marquise or asscher cut diamonds.
The dimensions are a matter of preference as well, but there are some fundamental issues with a diamond being too deep or too shallow (high depth relative to length and width), or having too elongated of a shape (high length relative to width). Each diamond shape is different but generally speaking our visual carat weight score will catch any major issues with these dimensions. You can check it for any GiA ID by using our GIA Check Tool to query your diamond.
2. GIA Grading Results (The 4 C's)
During your diamond research you may have come across the term "The 4 C's". This is diamond talk for the 4 most commonly discussed diamond grading criteria: carat, color, clarity, and cut. These 4 c's are covered in this second section:
- Carat Weight: a measure of a diamonds weight where 1 carat is equal to 0.2 grams. While this is often thought of as the "size" of a diamond, a more relevant measure would be the length and width since two diamonds can weigh the same in carats but appear different to the human eye based on their dimensions. StoneAlgo's visual carat weight calculation helps translate the length and width into an easy to understand carat weight equivalent.
- Color Grade: diamond color grades range from D to Z with D color diamonds being totally white and Z color diamonds typically appearing yellow or brown in color. The most common color grades for diamond jewelry are D - K, with D being the rarest and most expensive.
- Clarity Grade: diamond clarity grades describe the significance of any imperfections in the diamond that could impact the appearance of the stone. The highest grade is FL for flawless.
- Cut Grade: the GIA assigns cut grades to round diamonds but not to "fancy shapes" like oval, cushion, or radiant cuts. The highest cut grade is Excellent cut, but StoneAlgo has created our own scoring system for evaluating diamond cut score on a 10 point scale to help complement the GIA's cut grading scale.
Advice: Generally speaking, we'd recommend you consider color grades D - K, clarity grades FL - SI1 (not SI2, I1, I2, etc.), and only Excellent cut diamonds if you're shopping for round brilliant cut stones. Carat weight is a matter of preference but we would recommend you find a diamond who's actual carat weight is very similar to our calculation of it's visual carat weight as this typically means the diamond was cut to maximize sparkle as opposed to yield.
3. Additional Grading Information
Beyond the 4 C's, these are the next most commonly understood diamond specs:
- Polish: after a diamond is cut into it's final shape, the stone is polished so it has a bright, smooth surface. The top grade of diamond polish is Excellent followed by Very Good, Good, Fair, and Poor
- Symmetry: a symmetrical diamond will look balanced while a diamond with a low symmetry grade (fair or poor) may look lopsided.
- Fluorescence: Some diamonds give off a fluorescent glow when exposed to UV light.
Advice: For polish we typically advise only very good or excellent polish and for symmetry we recommend Excellent or Very Good symmetry for fancy shapes and only Excellent symmetry for round diamonds. Fluorescence is a bit of a matter of preference and we've written about how it can affect the diamond's price and the appearance of color in the stone in our Diamond Fluorescence Guide. We tend to recommend None or Faint fluorescence for diamonds that are D - F color and None, Faint, or Medium fluorescence for G - K color diamonds.
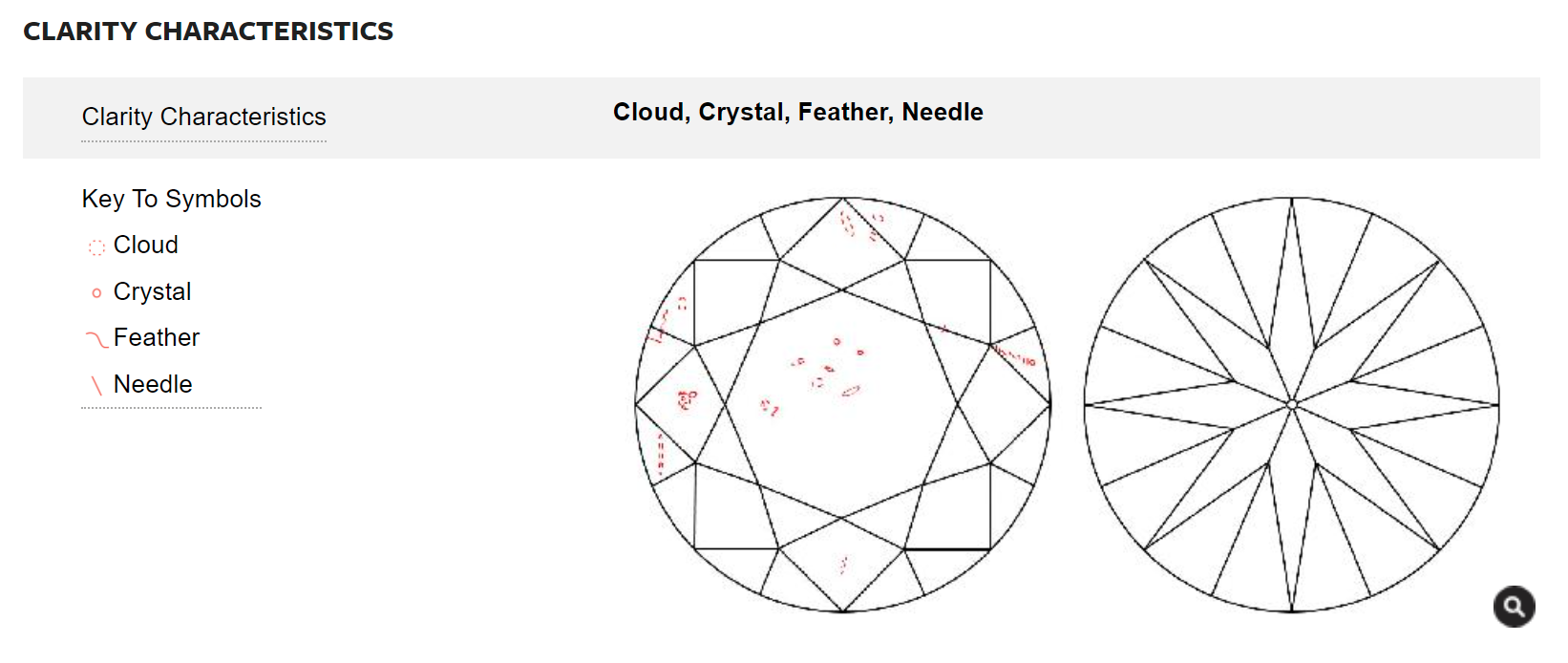
4, 6, 7. Understanding Inclusions On A GIA Certificate
Bear with us as we skip by the 5th section from the GIA report for a moment and look at 3 sections specifically related to diamond clarity. These 3 sections are:
- Key to symbols
- Comments
- The Diamond Plot
1. Key to symbols 2. Comments 3. Plot
First, we want to understand which inclusions are most significant.
The Key to Symbol section (#1 above) shows relevant inclusions listed in order of importance. In the example above, the most significant inclusion is a "Cloud". Below is a copy of the clarity characteristics and plot from the GIA's Certificate Lookup Tool. As you can see, next to each word in the key to symbols list is a special image that designates the inclusion. These symbols are then drawn on the diamond plot (#3 above) to show the location and size of the inclusions.
The Comments on the GIA Certificate (#2 in the certificate image shown earlier) are typically used to describe inclusions that could not be documented very well on the diamond plot at right. Most comments are not worth worrying over, but some are deal breakers. For example, you should always avoid the comment "Clarity grade is based on clouds that are not shown" in diamonds SI1 clarity or lower (SI2, I1, I2, etc.). This comment means that the grade setting inclusion is a significant cloud that is affecting the diamond's appearance. This means the diamond may look cloudy and that the sparkle of the stone is being affected by clouds inside the diamond.
5. Diamond Proportions
The diamond's proportions measure the various widths and angles of a diamond to help you better understand the cut quality of the stone. However, it's very difficult to evaluate a diamond's cut quality simply by looking at these dimensions which is why StoneAlgo uses all of these details to produce our diamond cut score and give a clearer measure of light performance and sparkle.
8. Grading Scales
Finally, on the far right of the certificate we have the GIA grading scales which outline the range of grades available for color, clarity, and cut. If you need more help evaluating your diamond check out StoneAlgo's dynamic research tools and comprehensive diamond search engine.
Check out our 100% free diamond check tool to automatically assess the quality and price of your diamond: